Factsheet: Gambia’s Debt To GDP Ratio Has Declined, But Does It Mean Prez Barrow Has Not Been Borrowing?
In his recent interview with the State of Affairs television programme on QTV, the Gambian leader Adama Barrow suggested his government has managed the country’s debt well by reducing it. “Our debt to GDP used to be 120%. Today, it is around 77%,” said President Barrow as he recounts his achievements. Rebasing of GDP It is accurate that Gambia’s public debt to GDP ratio was at 120% by the end of 2016. It is also correct that the current debt to GDP ratio is at 77.2%, according to the International Monetary Fund. But after the regime change in 2017, the government of Adama Barrow rebased the GDP, which led to a revision of the...
In his recent interview with the State of Affairs television programme on QTV, the Gambian leader Adama Barrow suggested his government has managed the country’s debt well by reducing it.
“Our debt to GDP used to be 120%. Today, it is around 77%,” said President Barrow as he recounts his achievements.
Rebasing of GDP
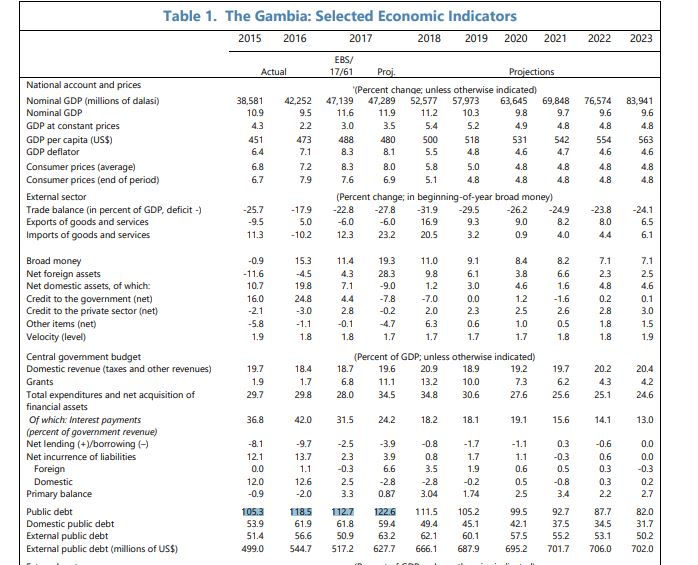
It is accurate that Gambia’s public debt to GDP ratio was at 120% by the end of 2016. It is also correct that the current debt to GDP ratio is at 77.2%, according to the International Monetary Fund.
But after the regime change in 2017, the government of Adama Barrow rebased the GDP, which led to a revision of the growth figures upwards from 3.5 percent to 4.6 percent in 2017.
Rebasing of GDP means replacing the old base year used for compiling the GDP with a new, more recent, base year for computing the constant price estimates.
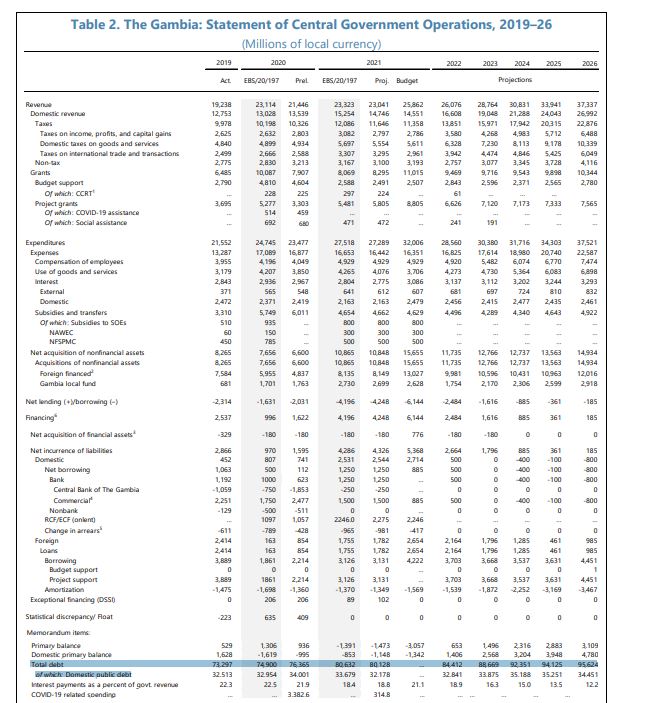
Hence, the increase in GDP brought the debt to GDP ratio down to 88%. This further declined, according to statistics from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to 77%.
An IMF report released in June 2021 stated a “decline of the public debt-to-GDP ratio (from 80.1 percent at end-2019 to 77.2 percent at end-2020).”
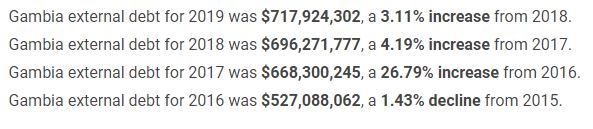
However, the actual debt (in numbers) inherited by President Adama Barrow did not decrease. Instead, it increased.
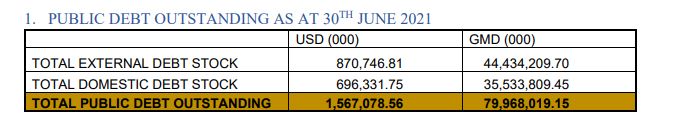
As at the end 2016, the public debt was D58 billion. But a more recent IMF report on Gambia published in June 2021, said the debt has increased from 73.2 billion in 2019 to 74.9 billion in 2020 and 80.6 billion in 2021, as of June.
The Finance Ministry’s debt bulletin published on their website recorded D79.9 billion as the country’s outstanding debt as of June.
Actual debt has increased under President Barrow from D58 billion to 80.6 billion as of June this year.
Conclusion
The reduction in Gambia’s debt to GDP ratio from 120% to 77.2% was due to the rebasing of the GDP and not because the current government has not been borrowing.